Lessons Learned
Backbone.js at SoundCloud
Darrell Stephenson - Front-End Engineer
Quick Assumptions
You know what Backbone.js is
You know what a single page application is
SoundCloud current stats
The platform reaches 200 million people every month
10 hours of audio are uploaded every minute
Single page app in production since December, 2012
~ 37,000 LOC. 80% of that is JS

Four Lessons
1. App Anatomy
2. Sharing between modular views
3. Efficient data representation
4. Cheating
Lesson #1
Application anatomy
An app in 5 parts
1. URLs route to layouts
2. Layouts insert high level views
3. Views can load and unload other views
4. Views know what data they need to render
5. Data is shared between views
Views are modular when they are composable, configurable and self-contained
app/views/group/info.js
var GroupInfo,
Group = require('models/group'),
View = require('lib/view');
GroupInfo = module.exports = View.extend({
className : 'groupInfo l-fixed',
css : require('views/group/info.css'),
template : require('views/group/info.tmpl'),
ModelClass: Group,
requiredAttributes: ['artwork_url'],
observedAttributes: ['member_count'],
getTemplateData: function (data) {
// modify data for template
return data;
}
});
app/views/group/sidebar.tmpl
<div class="sc-border-dark">
{{$view "views/group/artwork" resource_id=options.resource_id}}
{{#if has_info}}
{{$view "views/group/info" resource_id=options.resource_id}}
{{/if}}
</div>
Balance: models, collections, views
33 Models
48 Collections
~200 Views
Lesson Learned
Modular views are really powerful
Most-used, but least built by Backbone
Will save you bytes in the long run as your codebase scales
Will establish the most convention in your project
More implementation details
Lesson #2
Sharing between modular views
Example
I am a view. Which views am I in?
Approach 1 - View event bubbling
Communicate between views in a hierarchy
Useful for simple messaging
No event namespacing soup
Works a bit like DOM events, but not attached to DOM
var GroupInfo,
Group = require('models/group'),
View = require('lib/view');
GroupInfo = module.exports = View.extend({
className : 'groupInfo l-fixed',
css : require('views/group/info.css'),
template : require('views/group/info.tmpl'),
ModelClass: Group,
bubbleEvents: {
'onFooEvent': 'onFooEvent'
},
onFooEvent: function (event) {
// respond to event
}
});
What if the views are not in the same hierarchy?
What is this state?
No url, no save, no validate, toJSON, etc.
It's not a standard Model class
Some logic is needed before mutating state
Approach 2 - State Machines
Light and added to views as a mixin
Calls mixed-in methods directly
Automatically uses the resource of the view its being mixed into
A single instance is shared across views regardless of where it was set up first
Responsible for a small but specific set of rules
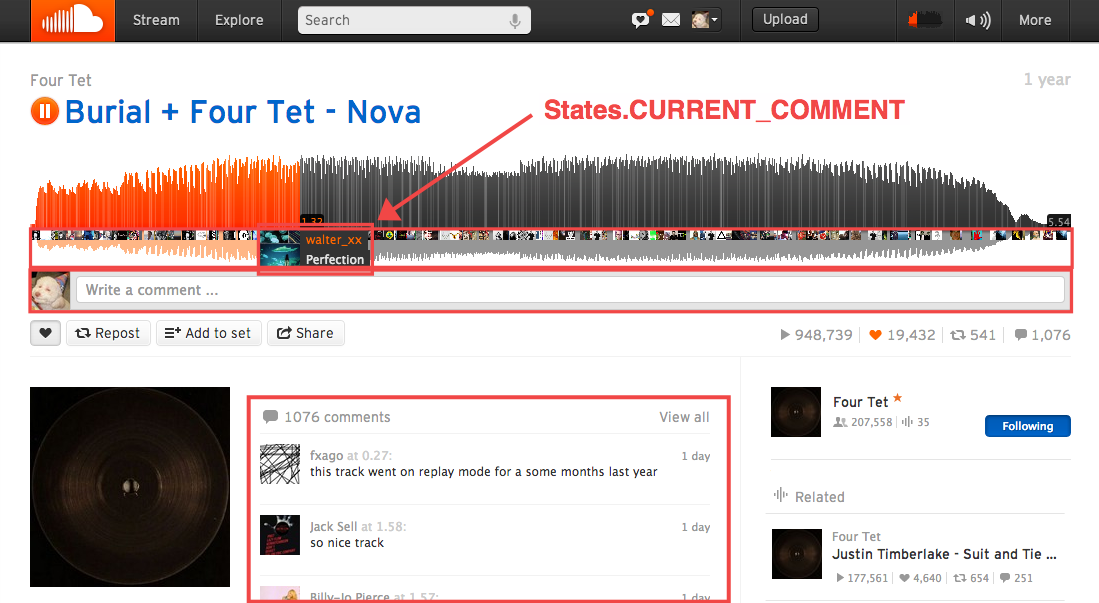
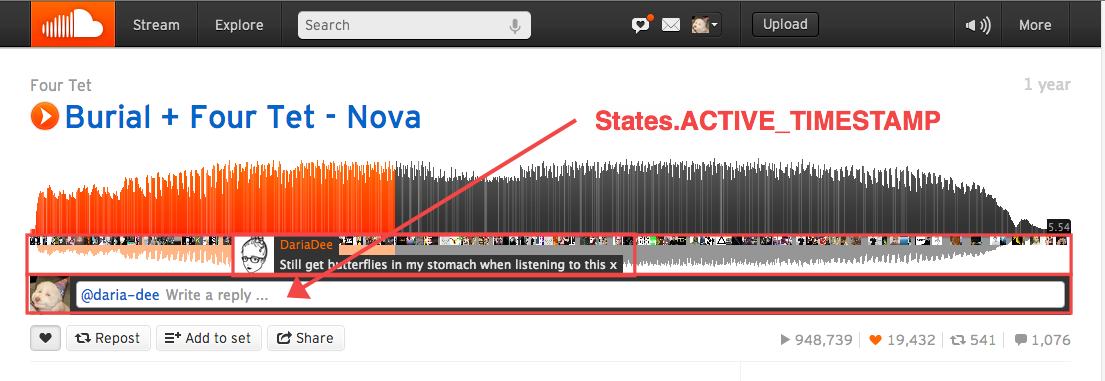
var CommentBubble,
TimedCommentsMixin = require('lib/views/mixins/timed-comments'),
View = require('lib/view');
CommentBubble = module.exports = View.extend(TimedCommentsMixin, {
// bind events, setup defaults, etc.
onCurrentCommentChange: function () {},
onCurrentTimestamp: function () {},
onActiveTimestamp: function () {},
onInitialState: function () {}
});
Lesson learned
Communication between isolated views is tricky
Want to share? Try event bubbling or state machines
Lesson #3
Efficient data representation
"Dogfooding"
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eating_your_own_dog_food
Using your product the same way a user would
We decided to "eat our own dogfood"
Good (/◔ ◡ ◔)/
The data is there. Lets go!
Concentrates common business logic
If the API can support our app it can support anything!
Bad ಠ_ಠ
Too generic to be fast at scale
Inflexible because of external obligations
Example
Lets load a set to display in a listing
The set also has 8 sounds in it that are in the response
Request to //api.soundcloud.com/playlists/1234.json
Size: uncompressed 27kb
What if we only need the basic information?
Example
Size: 572 bytes
Multiply x 10: 270kb vs 5.7kb
Multiply by millions of users
Change the dogfood!

We cant.

When you can't change the dog food
Client code gets the brunt of it
More complexity on the client
More expensive operations on the client
More requests to the API
Example 2
Waveform data
Change the representation
{
"width": 1800,
"height": 140,
"samples": [46, 62, 76, 80, 73, ...] // length === 1800
}
Dramatic results
UI was tangibly more responsive
From (╯°□°)╯︵ ┻━┻ to ~ 10 ms
Lesson learned
Using the public API doesn't work well at scale
Use flexible services without external obligations
Serve up good food and feed your app efficiently
Lesson #4
Cheating
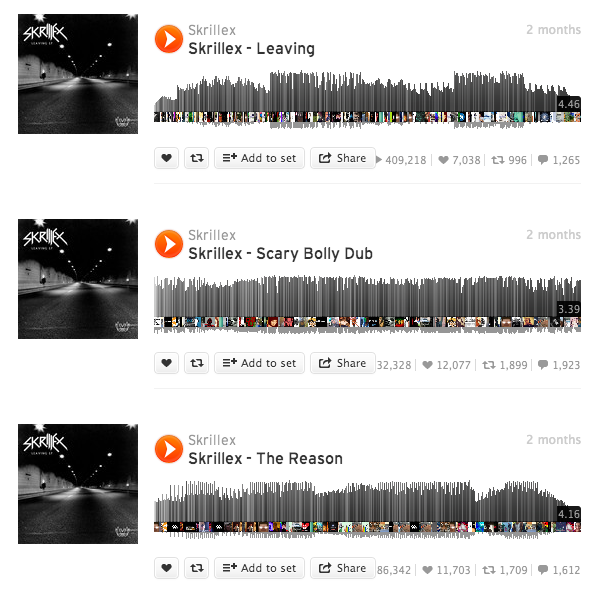
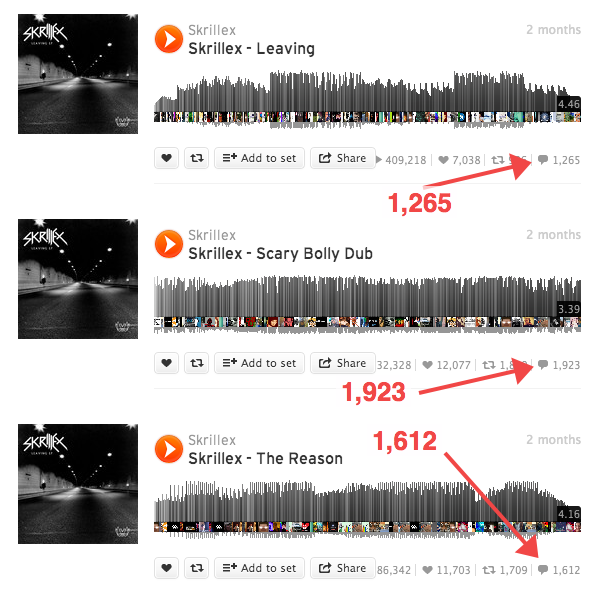
Standard setup totals
4800 comments : 1,265 + 1,923 + 1,612
4080 comments : Without 15% replies and offscreen
Initial template-based approach
Worked fine on low counts. Displayed within a list view class
Each list item makes 4 nodes. li > a > img + span
16,320 nodes : 4080 * 4 : only 3 sounds
~272,000 nodes / stream : 50 sounds * (1,360 avg comments / sound * 4)

Limit-enforced template approach
40,000 nodes / stream : 50 sounds * 200 comments per * 4 nodes per

Back To The Canvas

"Templates? Where we are going we don't need templates."
Waveform comments canvas
Just 1 node per sound. Handles any amount of comments
No template just a this.context reference
Same patterns for collection events
Preloads avatars with an array of deferred objects and draws avatars in a single loop when resolved
Separate views sit on top to provide an interaction layer
Going even further
Limit to last x comments
Draw last x commenter avatars ...
but draw the correct amount of lines in a repeatable way

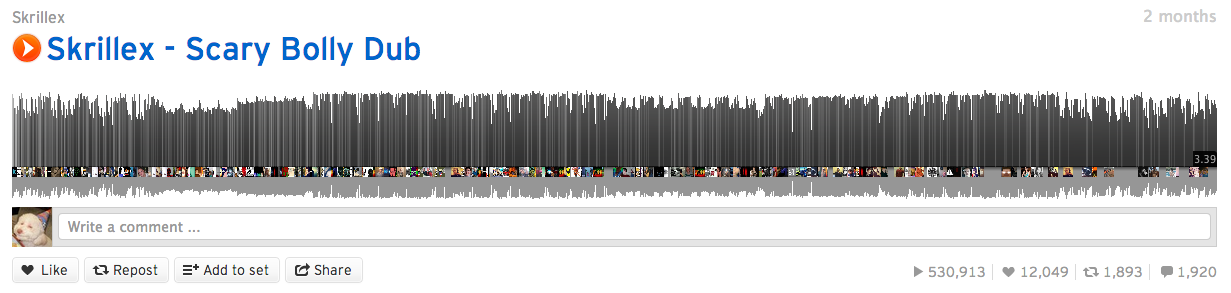

Hold up, wait a minute
Not a magic bullet for performance
Fits this use case really well
Example 2

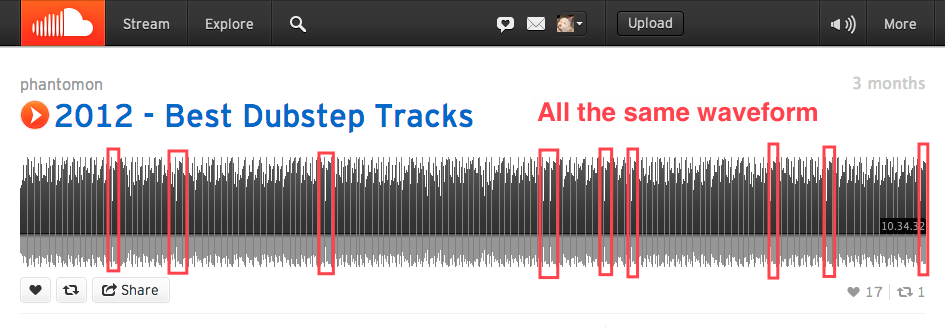
Shh ...
If the view is compressed into a very small space draw a fake
Choose from a pool of pre-selected waveforms, possibly cached on the client
Page is much faster, nobody can tell, everybody wins
Lesson learned
Break out of the standard view pattern where it makes sense
Backbone's view opinion is flexible enough to support this
Hack perception when possible. It's one of the most fun things in front-end development
Conclusions
A modular view system is the most important tool for building out your app.
Event bubbling and state machines can help share data between views.
Use efficient data structures and services you can adjust easily.
Cheating is fun and illusions can be as good as the real thing.
Thanks!
We are hiring! : Questions? @futuredarrell